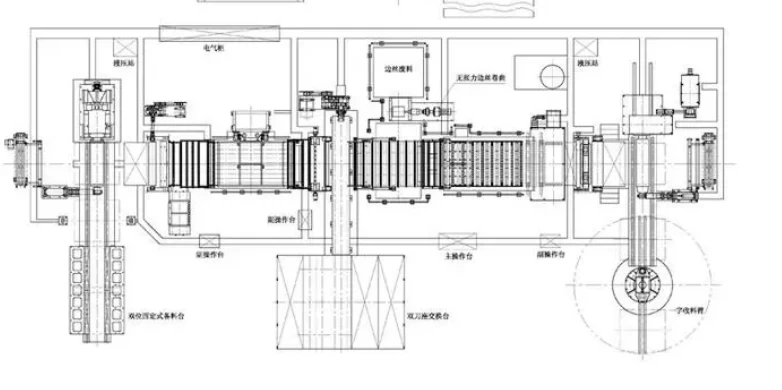
Galvanised sheet metal process
The main process of galvanised sheet
Coiling → double uncoiling → cutting head and tail → welding → alkali washing → primary brushing → → electrolytic cleaning → secondary brushing → hot water rinsing → hot air drying → inlet jacket → continuous annealing → hot dip galvanising (ceramic zinc pot) → air knife blowing (introduction) → → post-plating air-cooling → water quenching → levelling machine (reserved) → tensile straightener → passivation (reserved fingerprint-resistant) → export jacket → oiling → shear → reeling → uncoiling → weighing → → Packing
Functions of each section of galvanising line
Cleaning section: Remove cold rolled lubricant and iron powder from the strip surface. Cleaning before the entrance sleeve facilitates the stable tracking of the strip in the entrance sleeve and avoids dents and scratches.
Entry live sleeve section: Provides an effective length of vertical live sleeve when the entry stop is welded, enabling the line to produce continuously.
Furnace section: Vertical continuous annealing furnace to achieve the specified annealing cycle.
Galvanising section: Strips are galvanised by immersing them in a molten zinc pot.
Leveller and tension straightener section: to improve properties.
Post-treatment section (passivation): Tandem two-roll coater with furnace and cooling unit for applying chromate solution against white rust and fingerprints.
Exit bushing section: Provides effective length of vertical bushing to keep the line running continuously when the exit section is stopped for slitting.